Rubber extrusion is a part forming process. During this process, a high-pressure extrusion machine forces synthetic or natural rubber materials through a shaped die in order to get it to take on its section profile, shape or cut. Read More…
Aero Rubber Co. offers exceptional quality and competitive pricing on all of our extruded rubber products. Aero Rubber Co. uses high quality rubber compounds such as, Neoprene, Viton, Silicone, EPDM, Polyurethane, Natural Rubber, and Thermoplastic Rubber.

At Kent Rubber Supply Co., we specialize in providing high-quality rubber tubing solutions to meet the diverse needs of our customers. With decades of experience in the industry, we take pride in offering a comprehensive selection of durable, reliable, and customizable rubber tubing products. Our tubing is designed to perform in a wide range of applications, including industrial, commercial, and...

National Rubber values quality, consistency, and fast delivery of our products. Our components are made from a variety of elastomers such as neoprene and silicone, and our team members are capable of turning your drawing into the part you need. Contact us today to tell us about your next project!

GSH Industries supplies rubber extrusions to a range of industries. We offer rubber in materials such as Neoprene, Viton®, Nitrile, Silicone & more. We have tooling ability to create intricate profiles ensuring rubber goods are of the highest quality.

More Extruded Rubber Manufacturers
Extruded rubber is a highly versatile manufacturing solution used across a vast array of commercial, industrial, and residential sectors due to its adaptability, resilience, and cost-effectiveness. When searching for high-performance sealing, insulation, or protective materials, extruded rubber products offer a reliable answer to many specific application needs.
What is extruded rubber used for? In commercial applications, extruded rubber profiles—such as weatherstripping, gaskets, and seals—are essential for effective environmental protection and durability. For example, in the automotive industry, rubber extrusions are integral components for sealing car doors, windows, trunks, and hoods, providing superior weatherproofing and noise reduction. By blocking water, dust, and air, these extrusions extend vehicle lifespan and enhance passenger comfort.
In the construction industry, extruded rubber seals and gaskets are used to fortify insulation and energy efficiency in buildings. Weatherstrips made from extruded rubber help prevent air leakage around doors and windows, thus lowering energy bills and improving indoor comfort. Specialized rubber extrusions are also employed for expansion joints, curtain wall gaskets, and glazing seals in both commercial and residential buildings to absorb movement and protect structural integrity.
Industrial applications for rubber extrusions are extensive. In manufacturing and processing facilities, extruded rubber is used in conveyor belts—forming the flexible yet durable edges required for smooth material transport. In heavy machinery, rubber extrusions are shaped into custom gaskets, O-rings, and seals, which maintain airtight and watertight conditions, prevent leaks, and support optimal machinery performance. The inherent resistance of rubber to harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stress makes it a preferred choice for equipment in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. Here, extruded rubber hoses, tubing, and protective covers ensure reliability and compliance with strict regulatory standards.
Wondering how rubber window seals enhance energy efficiency in your home or business? In residential settings, extruded rubber weatherstripping is crucial for reducing drafts and maintaining comfortable indoor environments. These seals are commonly installed around doors, windows, and even in appliance doors (like refrigerators and ovens) to prevent leaks and improve insulation. In plumbing, rubber gaskets and seals made via extrusion guarantee reliable joints, preventing water leaks and ensuring consistent flow. Extruded rubber can also be found in garage doors, shower enclosures, and as edge trim and bumpers for various household applications.
Overall, extruded rubber solutions offer a cost-effective way to seal, cushion, and protect against environmental hazards. Their widespread use in sealing, gasketing, vibration dampening, and insulation boosts product performance, energy efficiency, and safety across a diverse range of commercial, industrial, and residential applications.
History of Extruded Rubber Manufacturing
Rubber, a naturally occurring elastomer derived from the Pará Rubber Tree, has been utilized by civilizations for centuries. Archeological evidence shows that as early as 1600 B.C.E., the Mayans extracted latex from rubber trees, refining it through boiling for the production of primitive rubber items.
The modern rubber extrusion process began in the 19th century, revolutionizing manufacturing by allowing natural and later synthetic rubber to be shaped into endless profiles for new applications. Early innovators began incorporating rubber into textile-based products, which marked a significant leap in industrial capability.
The scientific quest for new rubber materials accelerated in the 20th century. In 1909, Bayer chemists in Germany successfully polymerized isoprene to produce synthetic rubber. The following year, Sergei Vasilievich Lebedev in Russia developed a process to synthesize rubber from butadiene, a critical advancement during World War I when natural rubber was scarce. These milestones set the stage for synthetic rubber’s pivotal role in global industry and wartime production.
In 1931, DuPont researchers synthesized neoprene, a durable and corrosion-resistant polymer ideal for automotive and industrial hoses, gaskets, and seals. The outbreak of World War II caused Allied nations to ramp up synthetic rubber production, as access to natural rubber sources was restricted by Axis powers. Synthetic rubber became crucial for manufacturing military vehicle tires, seals, and essential mechanical components.
After the war, synthetic rubber production continued to grow, and by the 1960s, it had overtaken natural rubber in global production and usage. Today, a broad spectrum of synthetic rubbers is available, enabling manufacturers to tailor extruded rubber profiles for virtually any commercial, industrial, or consumer application.
Materials Processed in Rubber Extrusion
The performance and suitability of extruded rubber products depend on the type of raw rubber selected, the extrusion process, and any secondary processing steps. Selecting the right rubber compound is crucial to meet application-specific requirements such as flexibility, chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and durability.
- Natural Rubber (Gum Rubber): Known for excellent flexibility and resilience, natural rubber offers outstanding resistance to acids, abrasion, and mechanical stress. Commonly used in shock-absorbing mounts, vibration dampers, and flexible seals, it is ideal for dynamic environments.
- Silicone Rubber: Renowned for its FDA approval and biocompatibility, silicone rubber is chemically inert and non-reactive to biological fluids. It maintains its properties across a wide temperature range (-67°F to 572°F), making it the material of choice for food processing, medical devices, and high-temperature industrial seals. Silicone extrusions are also favored for electrical insulation and LED lighting gaskets.
- Viton (Fluoroelastomer): Viton is celebrated for its exceptional resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering, making it indispensable in harsh environments. It is widely used for seals, gaskets, and O-rings in aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing industries where exposure to aggressive fluids is common.
- Nitrile (NBR, Buna-N): Nitrile rubber is a synthetic copolymer prized for its superior oil and fuel resistance. It is extensively used in the automotive and hydraulic sectors for manufacturing O-rings, hoses, and hydraulic seals that must withstand exposure to petroleum-based fluids. Nitrile is also known as acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, Perbunan, or Buna-N.
- Neoprene: Neoprene rubber boasts excellent resistance to heat, fire, UV rays, water, and oil, along with high tensile strength. It is commonly used for weatherstripping, industrial hoses, and automotive gaskets where durability and environmental resistance are critical.
- Butyl: Butyl rubber features extremely low gas permeability, making it ideal for airtight seals, inner tubes, and protective membranes in chemical storage tanks and HVAC systems.
- SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber): SBR is valued for its outstanding abrasion resistance and is commonly employed in automotive motor mounts, belt covers, and flooring applications.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): EPDM rubber offers remarkable resistance to heat, ozone, UV rays, aging, and oxidation. Its versatility makes it suitable for sponge and foam rubber, weatherstripping, tarp straps, door and window gaskets, and roofing membranes. EPDM is highly regarded for outdoor and high-temperature applications.
Not sure which rubber compound is right for your application? Ask: What are the best rubber materials for high-temperature, chemical-resistant, or outdoor environments? Our experts can guide you through the selection process to ensure optimal performance and longevity for your extruded rubber components.
Rubber Extrusion Process Details
The rubber extrusion process involves several precise steps, each of which impacts the final product’s quality and performance.
- Pre-Heating (Optional): Rubber stock may be pre-heated to a molten state for hot extrusion, or remain at room temperature for cold feed extrusion, depending on the application and material.
- Material Feeding: Unvulcanized rubber is loaded into a hopper, positioned above the extruder’s conveyor system.
- Transfer to Conveyor: Gravity guides the rubber stock from the hopper into the conveyor channel.
- Advancement by Screw Mechanism: A rotating screw within the conveyor applies pressure and friction to heat and propel the rubber toward the die.
- Die Shaping: Once the material is sufficiently softened, it passes through the die, where it expands and adopts the desired cross-sectional profile.
- Profile Formation: The extruded rubber, now shaped according to the die, emerges from the extruder and cools into its final form.
Interested in how the extrusion process can be customized for your specific needs? Explore: What are the steps of the rubber extrusion process, and how do they affect product quality?
Post-Processing Techniques
Following extrusion, rubber profiles may undergo several secondary operations to enhance their properties or prepare them for end use:
- Vulcanization: This mandatory step cures the rubber using sulfur or other agents, greatly increasing strength, elasticity, and heat resistance.
- Dusting: Prevents freshly extruded parts from sticking together.
- Cutting and Drilling: Profiles are cut to precise lengths and, if necessary, drilled for attachment points or custom features.
- Coiling and Splicing: For continuous applications, extruded profiles may be coiled or spliced for seamless installation.
- Taping: Used to join ends or reinforce profiles as needed.
Vulcanization is especially critical in ensuring that rubber extrusions meet the mechanical and chemical performance requirements demanded by most industries.
Key Design Considerations for Extruded Rubber Products
When designing extruded rubber components, manufacturers must account for several critical factors:
- Material Selection: Choose a rubber compound with physical and chemical properties aligned to the operational environment (e.g., temperature extremes, exposure to oils or chemicals, UV exposure, or mechanical wear).
- Profile Geometry: Accurate die and tooling design ensures the cross-section matches functional requirements—whether for sealing, cushioning, vibration damping, or structural support. Considerations include solid vs. hollow profiles and precise dimensional tolerances.
- Process Optimization: Fine-tuning extrusion parameters (temperature, screw speed, pressure) is essential for consistent quality and to avoid defects such as voids or bubbles.
- Quality Control: Rigorous inspection and testing (dimensional checks, tensile strength, hardness) guarantee finished products meet both industry standards and customer specifications.
- Cost Management: Efficient material use, streamlined production, and minimized waste all contribute to cost-effective manufacturing.
- Environmental and Regulatory Compliance: Selecting sustainable rubber materials and implementing eco-friendly waste management practices help manufacturers adhere to environmental laws and industry certifications.
Looking for help optimizing your product design? Consider: What are the most important design factors for custom extruded rubber gaskets, seals, and profiles?
Machinery Used in Rubber Extrusion
Rubber extrusion relies on specialized equipment engineered for consistency, efficiency, and flexibility. The two main components are:
- Shearing Screw Conveyor: This heated conveyor contains a robust screw mechanism, which shears, mixes, and advances the rubber material through the barrel. The controlled heating and pressure facilitate material plasticization and uniform flow toward the die.
- Extrusion Die: The die is a precision-engineered chamber that shapes the rubber as it exits the extruder. Dies can be custom-manufactured to produce profiles of virtually any size or complexity, from simple U-channels to intricate multi-cavity seals.
What type of extrusion machinery is best for your project? Find out: How do different extruder designs and die configurations impact the final rubber product?
Variations and Related Manufacturing Processes
While traditional rubber extrusion is suitable for many applications, alternative and hybrid manufacturing processes can be leveraged for specialized needs.
- Injection Molding: This process involves heating rubber to a molten or pliable state and injecting it into a precisely shaped mold cavity. Injection molding is ideal for complex geometries, high-volume production runs, and applications requiring intricate part details. It is commonly used for elastomers, thermosetting polymers, or parts where high dimensional accuracy is essential.
- Plastic Extrusion: Similar in principle to rubber extrusion, plastic extrusion processes plastic pellets or granules into continuous profiles for tubing, piping, or custom plastic components. Post-extrusion, secondary processes such as cutting, drilling, or welding may be performed.
- Co-Extrusion: This advanced process enables the simultaneous extrusion of two or more rubber compounds, creating profiles with combined properties (e.g., a soft sealing face bonded to a rigid carrier). Co-extrusion is commonly used in automotive weatherstripping, building fenestration systems, and multi-function gaskets.
Trying to decide between extrusion and injection molding for your application? Compare: Which is better for your needs—rubber extrusion or injection molding?
Benefits of the Rubber Extrusion Process
Rubber extrusion offers a host of advantages that make it a preferred solution for manufacturing custom seals, gaskets, and profiles.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Rubber extrusion optimizes raw material usage, minimizes production waste, and lowers per-unit costs. The process supports high-volume runs, providing economies of scale that benefit both manufacturers and customers.
- Customizability: The ability to extrude rubber into virtually any continuous shape, length, or cross-section allows manufacturers to deliver bespoke solutions tailored to each client’s exact requirements. It facilitates unique designs for specialized industrial, commercial, and consumer applications.
- Continuous Production: Extrusion enables the creation of long, seamless profiles without the need for additional joining or assembly. This leads to stronger, more reliable products with consistent structural integrity.
- Superior Sealing Performance: Extruded rubber profiles offer exceptional resistance to air, water, dust, and other environmental contaminants, making them ideal for demanding gasketing and sealing applications.
- Environmental and Chemical Resistance: Rubber materials used in extrusion can be engineered to withstand harsh chemicals, UV light, ozone, and extreme temperatures, expanding their utility across challenging environments.
- Shock and Vibration Absorption: The inherent elasticity and damping properties of rubber make extruded profiles highly effective at absorbing impacts and reducing vibration or noise—a key consideration in automotive, aerospace, industrial, and construction uses.
- Easy Installation: The flexibility and resilience of extruded rubber products make them simple to handle and install, reducing labor time and costs on-site.
- Sustainability: Many rubber compounds used in extrusion are recyclable, supporting green initiatives and reducing environmental impact.
Still curious about the advantages of rubber extrusion? Discover: What are the key benefits of using extruded rubber for sealing, insulation, and protection?
Choosing the Right Rubber Extrusion Manufacturer
Selecting a reliable rubber extrusion supplier is a critical step in ensuring product quality, performance, and timely delivery. In a crowded marketplace, how do you identify the best partner for your project?
- Research Manufacturer Capabilities: Review company profiles, certifications, and case studies to verify experience in producing the types of extruded rubber profiles you require. Look for evidence of expertise in your industry (e.g., automotive, construction, medical, or electronics).
- Request Technical Support: A reputable manufacturer will offer design assistance, material selection guidance, and prototyping services to help refine your concepts and ensure manufacturability.
- Evaluate Communication and Customer Service: Initial responsiveness and clarity during discussions often reflect a company’s ongoing commitment to customer satisfaction. Avoid suppliers who are unresponsive or vague about specifications, lead times, or pricing.
- Assess Production Capabilities: Ensure the manufacturer can handle your required volumes, custom profile complexity, and any secondary processing needs (cutting, splicing, adhesive application, etc.).
- Check Quality Assurance Procedures: Ask about quality control protocols, testing certifications, and guarantees to ensure finished products will meet or exceed your expectations and industry regulations.
- Compare Quotes and Lead Times: Balance price with quality, reliability, and service. The lowest cost may not always represent the best overall value if it comes at the expense of quality or timely delivery.
Ready to start your search? Ask yourself: What are the most important criteria for selecting a rubber extrusion manufacturer for my application? We’ve curated a list of trusted manufacturers, each with proven expertise and a reputation for customer satisfaction. Begin by exploring their offerings, then narrow your choices to the leading candidates. Reach out to discuss your project in detail—covering technical requirements, order quantities, budget, and delivery expectations. Carefully evaluate each interaction, prioritizing clear communication and a willingness to address your specific needs. By following these steps, you can confidently select a manufacturing partner who will deliver quality results and reliable service for your extruded rubber projects.
Have more questions? Contact our experts to discuss your specific rubber extrusion needs, request a quote, or get help with material selection and product design.
What is extruded rubber used for?
Extruded rubber is widely used for sealing, insulation, and protection in commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. Common applications include automotive weatherstripping, gaskets, and seals for doors and windows, industrial conveyor belts, machine gaskets, expansion joints in construction, as well as weatherstripping and bumpers in household and appliance settings.
What rubber materials are best for high-temperature, chemical-resistant, or outdoor environments?
For high-temperature applications, silicone rubber is recommended due to its broad temperature tolerance. Viton (fluoroelastomer) offers superior chemical and weather resistance, making it ideal for harsh, chemical-rich environments. EPDM is highly valued for outdoor use thanks to its excellent resistance to heat, UV rays, ozone, and weathering.
What are the steps of the rubber extrusion process and how do they affect product quality?
The rubber extrusion process involves pre-heating (if needed), material feeding, transfer to the conveyor, screw-driven advancement, shaping through a die, and profile formation. Each step impacts consistency, precision, and mechanical properties. Post-processing steps like vulcanization, dusting, cutting, and splicing further enhance durability and performance.
What are the most important design factors for custom extruded rubber gaskets, seals, and profiles?
Key design considerations include selecting the proper rubber compound for the operating environment, precise profile geometry for the desired function, process optimization to avoid defects, rigorous quality control, cost management, and ensuring compliance with environmental and industry regulations.
How do different extruder designs and die configurations impact the final rubber product?
The extruder design, especially the type of screw and heating capabilities, affects material mixing and consistency. Custom die configurations determine the final shape, cross-sectional accuracy, and complexity of the extruded profile, enabling the production of anything from U-channels to multi-cavity seals tailored to specific applications.
Which is better for your needs—rubber extrusion or injection molding?
Rubber extrusion is suited for creating long, continuous profiles with custom cross-sections, making it ideal for weatherstripping, gaskets, and seals. Injection molding is better for complex, three-dimensional parts and high-volume production of intricate shapes where high dimensional precision is required.
What are the key benefits of using extruded rubber for sealing, insulation, and protection?
Extruded rubber offers cost-effectiveness, versatility in shapes and sizes, seamless continuous production, superior sealing performance, resistance to environmental and chemical exposure, vibration and shock absorption, easy installation, and sustainability through recyclable materials.
What are the most important criteria for selecting a rubber extrusion manufacturer for my application?
Important criteria include the manufacturer’s proven experience in your required profiles and industry, available technical support, responsiveness and communication, production capability for your quantities and complexity, quality assurance procedures, and a balanced assessment of quotes and lead times.






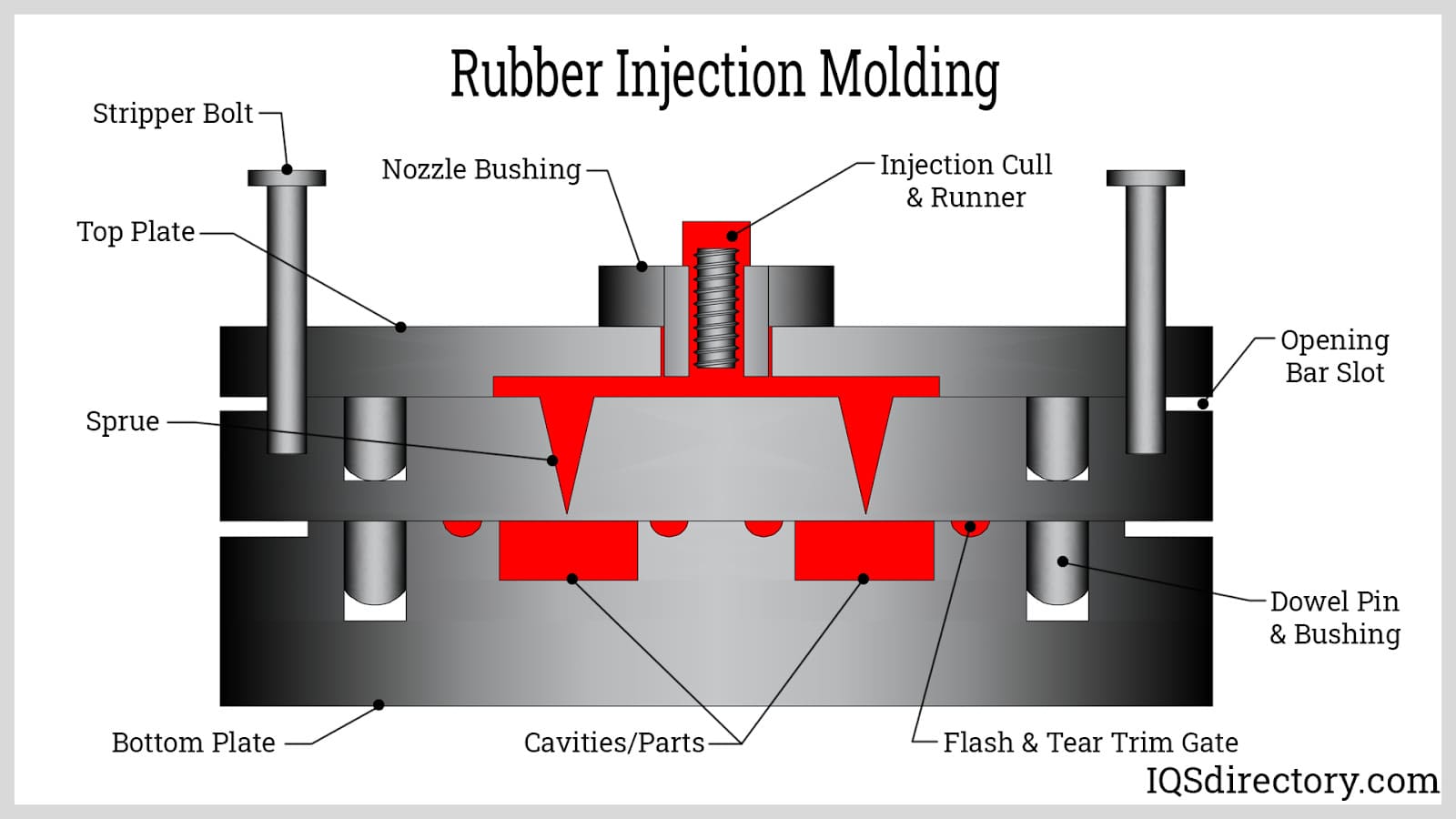


 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services