Rubber extrusion is a part forming process. During this process, a high-pressure extrusion machine forces synthetic or natural rubber materials through a shaped die in order to get it to take on its section profile, shape or cut. Read More…
Aero Rubber Co. offers exceptional quality and competitive pricing on all of our extruded rubber products. Aero Rubber Co. uses high quality rubber compounds such as, Neoprene, Viton, Silicone, EPDM, Polyurethane, Natural Rubber, and Thermoplastic Rubber.

Since 1976, Lakeview Industries has been globally known for manufacturing rubber extrusions. Our die cut equipment and fabricated rubber products such as rubber grommets and rubber bumpers provide the environmental sealing and noise control industries with reliable molded rubber products. We do both standard and custom profiles to help meet your rubber requirements.

GSH Industries supplies rubber extrusions to a range of industries. We offer rubber in materials such as Neoprene, Viton®, Nitrile, Silicone & more. We have tooling ability to create intricate profiles ensuring rubber goods are of the highest quality.

At American Rubber Products, we take pride in our expertise and commitment to delivering top-notch rubber extrusions. With decades of collective experience, we specialize in providing high-quality solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of our diverse clientele. Join us on the journey of excellence, where passion and proficiency converge to create unparalleled rubber extrusion solutions that...

We got our beginning in 1954 and ever since then we have been manufacturing custom rubber extrusion solutions for customers around the world! We are a family and employee owned business dedicated to ensuring that our customers are receiving customer care that cannot be matched by the competition! Visit our website today to learn more about what we may be able to do for you!

More Extruded Rubber Manufacturers
Extruded rubber boasts extensive applications across commercial, industrial, and residential domains owing to its adaptability and resilience. In commercial settings, particularly in automotive contexts, rubber extrusions play a pivotal role in sealing and weatherproofing vehicles. By effectively barring water, dust, and noise from infiltrating cabins, these extrusions uphold vehicle integrity. Moreover, in construction, they are indispensable for sealing doors and windows, fortifying insulation, and bolstering energy efficiency within buildings.
Rubber extrusions are indispensable in industry, serving pivotal roles across diverse applications. They are crucial in manufacturing conveyor belts, forming the edges that ensure seamless material transport with efficiency. Additionally, in heavy machinery, rubber extrusions are instrumental in crafting gaskets, seals, and O-rings, which maintain crucial airtight and watertight seals, thereby preventing leaks and sustaining machinery performance. Rubber’s resilience to chemicals and extreme temperatures further enhances its utility in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and food processing. Here, it finds application in hoses, tubing, and protective covers, where its durability and versatility are paramount.
Rubber extrusions play a crucial role in enhancing residential environments by promoting safety and comfort. For instance, weatherstrips crafted from rubber extrusions are installed around doors and windows, effectively minimizing drafts and bolstering energy efficiency within households. Moreover, they are integral components in home appliances like refrigerators and ovens, functioning as seals and gaskets to uphold insulation and prevent leaks. In household plumbing systems, rubber extrusions are widely employed to create reliable seals and gaskets, thus preventing water leaks and maintaining consistent water flow.
Rubber extrusions provide a cost-effective solution across commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. They excel in sealing, cushioning, and protecting against environmental factors, playing a crucial role in enhancing product performance, energy efficiency, and safety across diverse applications.
History
Rubber, a naturally occurring elastomer derived from the Pará Rubber Tree, has been cultivated since ancient times. Evidence suggests that as early as 1600 B.C.E., the Mayans were extracting latex from rubber trees and refining it through boiling to create a primitive form of rubber. However, the modern rubber extrusion process, which involves shaping natural and synthetic rubber materials into various products, did not emerge until the 19th century. It was during this period that manufacturers started incorporating rubber into textile profiles, marking a significant advancement in industrial applications.
In the early 20th century, scientists embarked on the synthesis of rubber. In 1909, Bayer researchers in Elberfeld, Germany successfully polymerized Isoprene. Soon after, in 1910, Sergei Vasilievich Lebedev, a Russian scientist, pioneered another synthetic rubber derived from butadiene. This innovation proved crucial for Russia during World War I, establishing synthetic rubber as a pivotal material.
In 1931, just before the onset of the Second World War, scientists at DuPont achieved a breakthrough by successfully synthesizing neoprene. This new polymer boasted exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making it particularly valuable for applications like vehicle fuel hoses. Its popularity soared, sparking a global race among scientists, primarily in the US, Germany, and the Soviet Union, to develop superior and more cost-effective neoprene-like polymers. With the outbreak of World War II, the United States intensified its production of synthetic rubber, responding to the scarcity caused by Axis control over much of the world’s rubber supply. Throughout the war, rubber materials played a crucial role in the construction of military vehicle tires and other essential war machinery components.
After the war, synthetic rubber production persisted and by the 1960s, it surpassed natural gum rubber in both production and usage. Today, the variety of synthetic rubber types has expanded significantly, with rubber extrusion playing a crucial role in countless consumer, commercial, and industrial applications across the globe.
Materials Processed
The characteristics of each final product hinge on the type of raw rubber stock used, the specific extrusion processes applied, and any subsequent secondary treatments. Given the diverse nature of rubber in its various forms, manufacturers of rubber extrusions can enhance their products by carefully selecting the raw materials.
Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, also known as gum rubber, is highly prized for its exceptional resistance to acids and abrasion.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber, certified by the FDA as a non-reactive elastomer, remains chemically inert and unresponsive to biological fluids. Its stability in form and properties persists across a wide temperature range, from -67℉ to 572℉. These exceptional characteristics make silicone highly favored in food service and healthcare applications.
Viton
This rubber compound exhibits exceptional heat, chemical, and weather resistance, making it highly sought-after in sectors such as food service and healthcare.
Nitrile
Nitrile, a versatile synthetic rubber copolymer, exhibits exceptional resistance to oils, making it ideal for manufacturing rubber products such as O-rings, hoses, and hydraulic seals that will come into contact with oils. It is also referred to by various names including nitrile rubber, NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber), acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, Perbunan, or Buna-N.
Neoprene
Neoprene exhibits exceptional resistance to heat, fire, UV rays, water, and oil, coupled with a notable high tensile strength.
Butyl
Butyl exhibits minimal air flow permeability.
SBR
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) boasts exceptional resistance to abrasion, making it a favored choice in various automotive applications such as manufacturing motor mounts and belt covers.
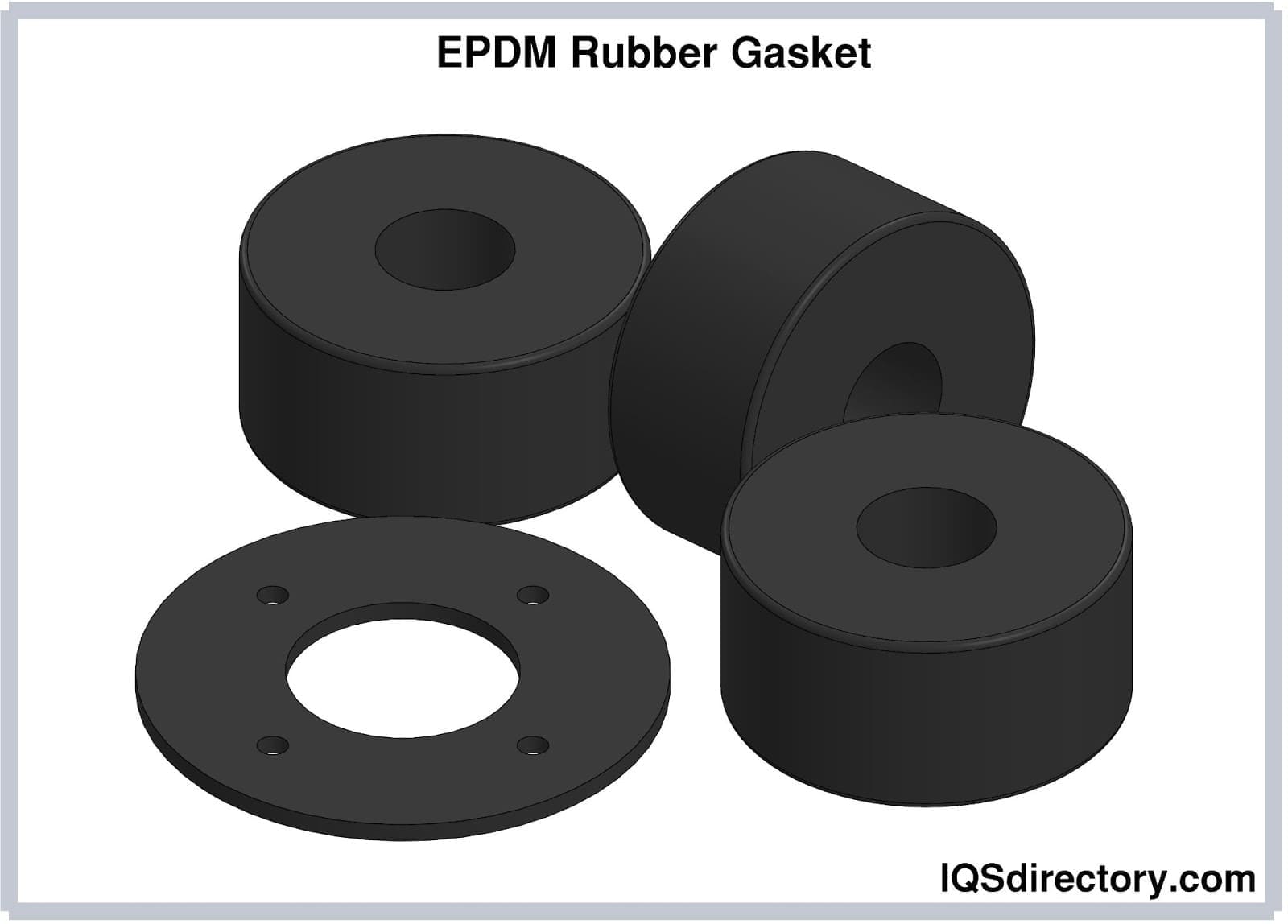
EPDM
EPDM, known as ethylene propylene diene terpolymer, exhibits remarkable resistance to various types of damage such as heat, aging, ozone, oxidation, and ultraviolet rays. Its versatile applications encompass sponge rubber, foam rubber, weather-stripping, tarp straps, door gaskets, window gaskets, and roofing membranes.
Process Details
After finalizing the design phase, which includes die creation and material selection, manufacturers proceed with standard rubber extrusion using a rubber extruder.
- Optional: Pre-heat the stock until it reaches a molten state for hot extrusion. Failure to do so results in what is known as “cold extrusion,” or, depending on the application, “cold feed extrusion.”
- Introduce unvulcanized rubber into the hopper, a container positioned above the conveyor.
- Utilize gravity to guide the rubber stock from the hopper’s bottom, directing it onto the conveyor.
- The conveyor, coupled with a rotating screw, advances the rubber towards the die. The screw applies both pressure and heat, aiding in the continuous propulsion of the rubber forward.
- Once it reaches the end of the conveyor and softens sufficiently, the rubber flows through the die’s opening.
- As the rubber flows through the die, it expands and molds into its final shape.
- After exiting the die, the rubber emerges from the extruder’s opposite end, transformed into a profile that mirrors the shape of the die.
Post-Processing
Once the rubber profile has been processed, various post-processing or secondary procedures can be undertaken. These include vulcanization, where the rubber is chemically treated for durability, dusting to prevent adhesion, cutting, drilling, coiling, splicing, and taping for joining ends. Vulcanization is mandatory among these processes.
Vulcanization
Vulcanization, a widely used process for enhancing extruded rubber, involves curing the rubber using sulfur or other curative compounds.
Design Considerations
Manufacturers tackling rubber extrusions must navigate several pivotal factors to ensure the creation of top-tier products that meet exacting standards. Foremost among these is the selection of suitable rubber materials. Each type of rubber compound presents distinct characteristics such as hardness, flexibility, chemical and weather resistance, as well as temperature endurance. Thus, manufacturers must meticulously opt for the rubber material that best suits the specific demands and performance criteria of the extruded item.
Another pivotal aspect involves crafting the extrusion profile’s design. Manufacturers must meticulously create profiles that precisely align with the intended shape and dimensions of the end product. This task encompasses evaluating design intricacies, necessary tolerances, and the practicality of the extrusion process. Moreover, design decisions extend to selecting the optimal cross-sectional geometry—whether solid or hollow profiles—to fulfill functional needs such as compression, sealing efficiency, or impact resistance.
Manufacturers must refine the extrusion process to maintain consistent product quality and efficiency. This entails pinpointing optimal extrusion temperatures, pressures, and speeds to ensure thorough rubber curing while preventing issues such as air bubbles or voids. Additionally, meticulous tooling design and upkeep play crucial roles in ensuring steady product output and reducing material waste.
Quality control in rubber extrusion manufacturing is vital. It involves stringent inspection and testing procedures to detect defects or deviations in the final product. This includes monitoring dimensional accuracy, hardness, tensile strength, and other key properties to ensure compliance with industry standards and customer requirements.
Cost considerations dominate manufacturing decisions, requiring manufacturers to strike a balance between raw materials, equipment, labor, and energy costs while aiming for optimal product quality and performance. Enhancing production processes, minimizing material wastage, and boosting efficiency are essential in achieving cost-effective rubber extrusion manufacturing.
Manufacturers must prioritize environmental and regulatory factors. Adhering to environmental laws and embracing sustainability initiatives has become paramount for businesses. Choosing eco-friendly rubber materials and adopting effective waste management strategies are vital for reducing the environmental footprint of rubber extrusion manufacturing.
Manufacturers face a complex landscape when creating rubber extrusions, balancing material selection, design efficiency, process optimization, quality assurance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact. Mastering these elements ensures the production of top-tier extruded rubber products tailored to diverse industry demands and applications.
Machinery Used
A typical rubber extruder, also known as a screw extruding machine, comprises two primary components: a heated screw conveyor for shearing and a die.
Shearing Screw Conveyor
The shearing screw conveyor consists of a conveyor aligned with a screw mechanism. This screw runs parallel to the conveyor, effectively pushing rubber material into the conveyor channel. Within this channel, the material undergoes heating, pressurization, and plasticization processes.
Extrusion Die
A die functions as a predefined chamber used in shaping materials. Pressurized and plasticized rubber is forced through this chamber to form specific shapes. At the end of a conveyor, the material is pushed by a screw into the die, where it takes on the desired form. After cooling, the rubber shape is considered “extruded.” Dies can be tailored to almost any shape, allowing rubber to be extruded into virtually any form, regardless of size or complexity.
Variations and Similar Processes
Different types of rubber extrusion vary depending on the rubber used. For instance, achieving successful silicone extrusion requires adjusting the extruder temperature to accommodate silicone’s heat-resistant properties. In contrast, preparing natural rubber for extrusion involves initially dividing it into pellets. Not all extrusions are limited to specific rubber materials.
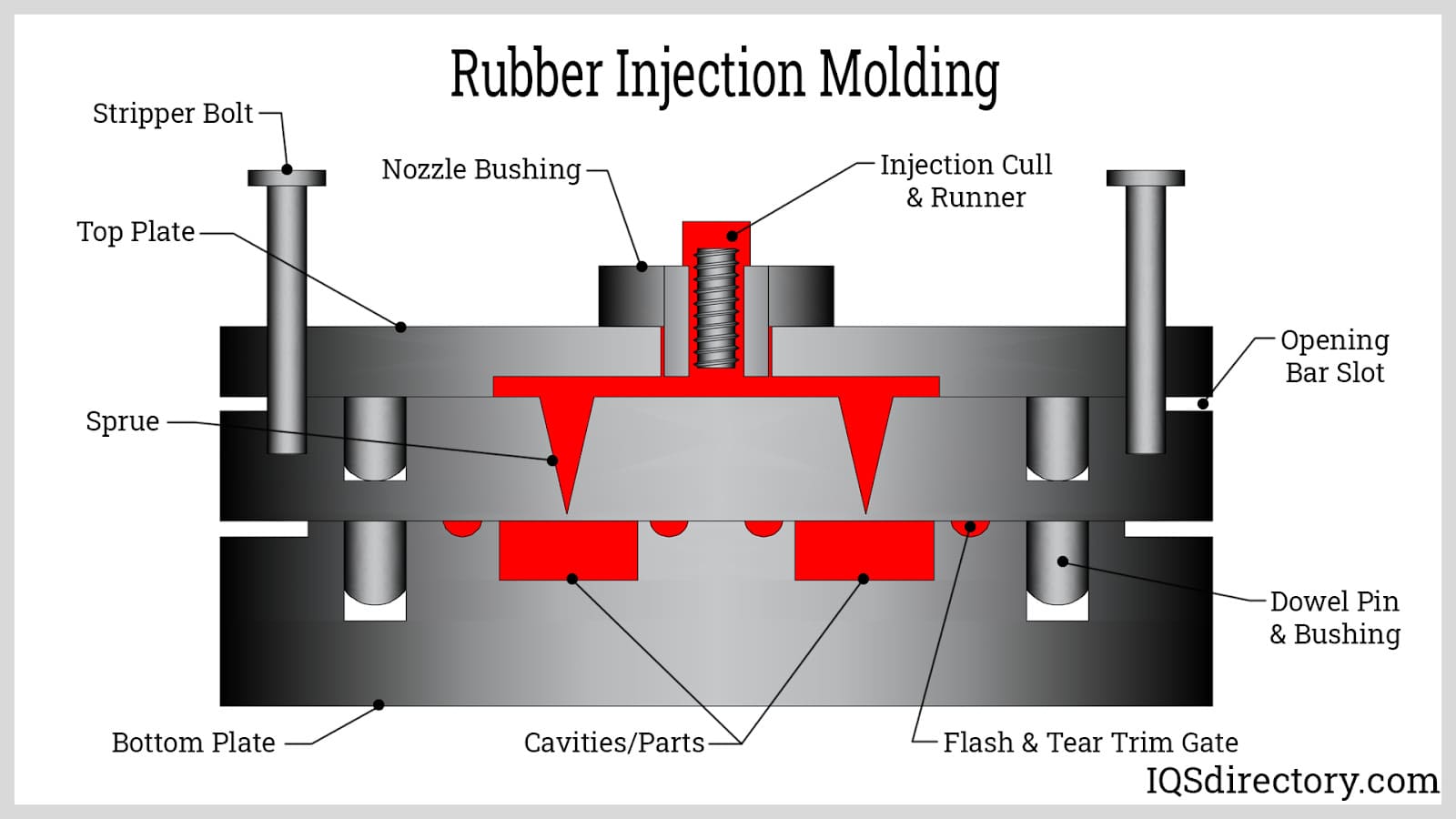
Injection Molding
Injection rubber molding offers a widely embraced alternative to rubber extrusion. This method involves heating the rubber material until it reaches a molten or warm state, which is then injected into a mold cavity. With the aid of heat and/or pressure within the mold cavity, the rubber adopts the precise shape of the mold before cooling and solidifying. Injection molding proves advantageous particularly for elastomers, thermosetting polymers, or intricate designs due to its capability to achieve complex geometries effectively.
Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion closely mirrors rubber extrusion. Initially, raw materials in the form of plastic nuggets or kernels are fed into a column containing a screw. Through this process, the material becomes semi-fluid and flows through a die. Following extrusion, the plastic parts undergo subsequent secondary processes tailored to their specific requirements.
Co-extrusion
Co-extrusion represents an advanced form of extrusion that enables the production of rubber parts with combined properties from multiple rubber materials. This process involves using two distinct extruders and batches of rubber, each with its unique mix, connected to a single die. Both batches of rubber are simultaneously fed into the die, allowing them to merge seamlessly. After cooling, these extruded rubber parts can be used directly or undergo additional treatments to enhance their properties as needed.
Benefits
Rubber extrusion stands out as a favored manufacturing technique across multiple industries, primarily due to its cost-efficiency. This method optimizes the use of raw materials, curtails waste, and diminishes production expenses. Moreover, it supports the creation of large quantities, ushering in economies of scale that significantly reduce the cost per item, making it especially advantageous for items produced en masse.
Rubber extrusion shines in its ability to mold into intricate shapes and profiles, opening a gateway for manufacturers to craft an array of products, each with unique cross-sectional geometries, dimensions, and lengths. This adaptability not only provides bespoke solutions but also caters to the nuanced demands of various sectors including automotive, construction, aerospace, and beyond.
The uninterrupted flow of the extrusion process stands as a notable benefit. Rubber can be shaped into extended lengths through extrusion, minimizing the need for extra assembly and eliminating weak spots that could compromise the product. This technique yields items that are not only stronger but also boast enhanced structural integrity, ensuring reliability and durability.
Rubber extrusions excel at crafting seals that are impervious to air, water, and dust, making them perfect for applications that demand tight, leak-proof barriers. Their capacity to form precise and uniform profiles guarantees a steadfast seal, thereby boosting the durability and efficacy of the products they protect.
Moreover, rubber extrusions boast remarkable resilience against diverse environmental threats such as chemicals, UV rays, and severe temperature fluctuations. This robustness renders them apt for numerous demanding scenarios, broadening their utility across various sectors.
Rubber’s natural cushioning and shock-absorption qualities make it an ideal choice for safeguarding against impacts and reducing vibrations. Products crafted via rubber extrusion excel in managing energy absorption and dispersion, proving indispensable in environments where impact resistance is crucial.
Additionally, the pliability of rubber extrusions makes them a favored choice due to their simplicity in installation. Their inherent flexibility facilitates effortless placement and alignment, thereby diminishing the time and cost associated with assembly.
The appeal of rubber extrusion is greatly enhanced by its environmentally friendly characteristics. The rubber materials often employed in the extrusion process are recyclable, aiding sustainability initiatives and minimizing the environmental impact of manufacturing.
In summary, the rubber extrusion process presents a wealth of advantages such as affordability, flexible design options, continuous production flow, dependable seals, robustness, protective qualities, straightforward installation, and eco-friendliness. These benefits make rubber extrusions an attractive option across various sectors, providing efficient and dependable solutions tailored to a multitude of needs.
Choosing a Manufacturer
To secure a superior product, partnering with a top-tier manufacturer is essential. In today’s digital deluge, discerning dependable companies from the dubious can be daunting. We’ve curated a list of esteemed rubber extrusion companies, each with a track record of exceeding customer expectations. Begin your journey by exploring their profiles, keeping your specific needs in mind. Narrow down your choices to three or four that catch your interest. Initiate conversations with these selected companies, discussing your specifications, requirements, and any queries you might have, particularly concerning order volumes, pricing, and delivery timelines. Evaluate each interaction carefully, weighing not just the financial aspects but also the quality of customer service. Opt to avoid manufacturers that fall short in communication, as poor service could lead to costly misunderstandings later. Once you’ve identified the ideal supplier, reach out to commence your partnership. Wishing you a fruitful collaboration!








 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services